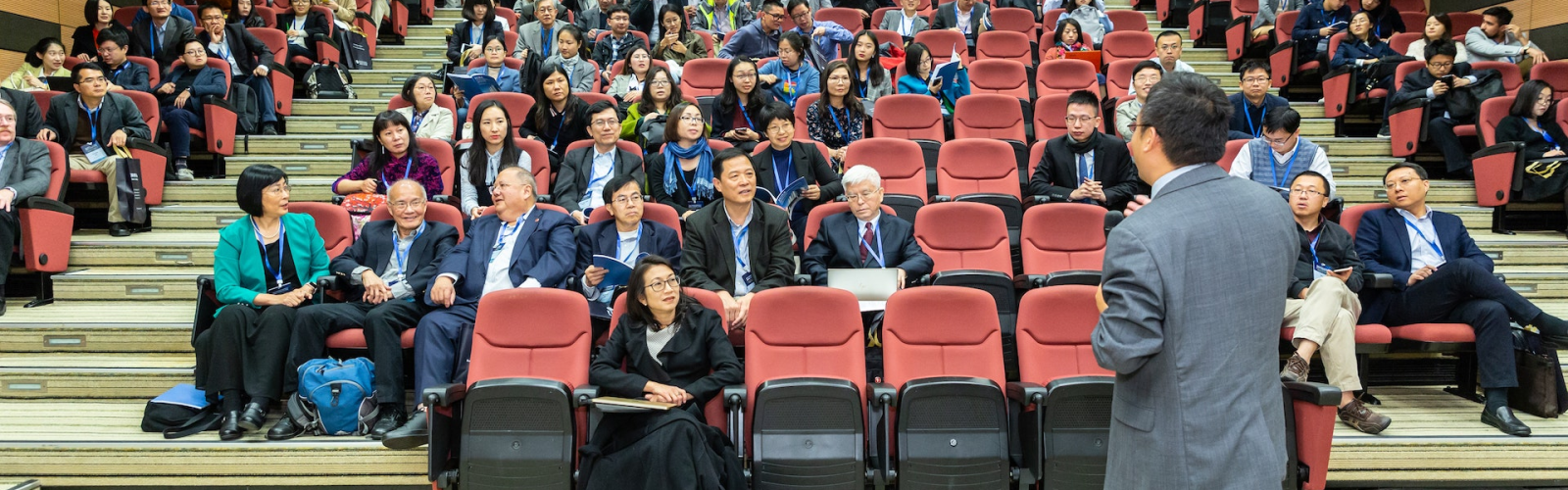
Italy is a country with a rich cultural heritage and a long history. With its beautiful cities, stunning natural landscapes, and delicious cuisine, it is no wonder that millions of tourists visit the country every year. However, it is important to be aware of the rules and regulations in place when visiting or living in Italy. These laws help to ensure the safety and well-being of all citizens and visitors. In this article, we will examine some of the most important rules and regulations in Italy, including those related to immigration, employment, and business.
Immigration Rules and Regulations
Italy is a member of the European Union (EU) and as such, citizens of other EU countries are entitled to live and work in the country without the need for a visa or work permit. Non-EU citizens, on the other hand, must obtain a visa in order to enter the country, and may also need to apply for a work permit if they wish to work in Italy.
The type of visa required will depend on the purpose of the visit. For example, if you are visiting Italy for tourism, you will need a tourist visa, while if you are visiting for business purposes, you will need a business visa. In some cases, you may need to provide proof of financial support, such as a bank statement or sponsorship letter, in order to be granted a visa.
In order to apply for a visa, you will need to complete an application form and submit it to the Italian embassy or consulate in your home country. You may also need to provide additional documents, such as a passport, travel itinerary, and proof of financial support.
Once you have entered Italy, you will need to apply for a permesso di soggiorno, or permit of stay, if you wish to remain in the country for more than three months. This permit will allow you to legally reside and work in Italy, and must be renewed every two years.
Employment Rules and Regulations
Italy has a highly regulated labor market, with strict laws in place to protect workers and ensure fair treatment. Some of the most important employment rules and regulations include:
-
Minimum wage: Italy has a minimum wage, which is currently €1,158 per month for full-time workers. Employers are required to pay at least this amount to their employees.
-
Working hours: The maximum number of working hours in Italy is set at 40 hours per week, and employees are entitled to a minimum of 11 hours of rest per day.
-
Vacation time: Italian workers are entitled to a minimum of 20 days of paid vacation per year, although many companies offer more.
-
Sick leave: Employees who fall ill are entitled to paid sick leave, with the amount and duration of leave depending on the nature and severity of the illness.
-
Maternity leave: Pregnant women are entitled to a minimum of five months of paid maternity leave, and may also be entitled to additional paid leave if they have children under the age of three.
-
Termination of employment: In Italy, employment contracts can be terminated by either the employer or the employee, but the process must be carried out in accordance with the law. For example, an employer must give an employee a minimum of three months' notice before terminating their contract.
In Italy, businesses are subject to a range of rules and regulations that aim to protect the interests of companies, workers, consumers, and the wider public. Some of the key business regulations in Italy include:
-
Labor laws: Employers in Italy are required to comply with a range of labor laws, including those covering minimum wage, working hours, health and safety, and vacation entitlements.
-
Taxation: Businesses operating in Italy must pay taxes in accordance with the country's tax laws, which include corporate tax, value-added tax (VAT), and other taxes on the sale of goods and services.
-
Data protection: Businesses must comply with Italy's data protection laws, which aim to protect the privacy of individuals and the security of their personal data.
-
Environmental regulations: Companies operating in Italy must comply with environmental regulations aimed at reducing the impact of their activities on the environment. This includes regulations covering waste management, air and water pollution, and the use of hazardous materials.
-
Consumer protection: Businesses must comply with consumer protection laws, which aim to ensure that products and services are safe and of good quality, and that consumers are treated fairly.
-
Anti-competition laws: Italy has laws in place to prevent anti-competitive behavior by businesses, such as price fixing, abuse of a dominant market position, and anti-competitive mergers.
-
Company formation and registration: Companies operating in Italy must be registered with the relevant authorities and comply with the country's company formation and registration requirements.
These are just some of the key business regulations in Italy. It's important for businesses to familiarize themselves with the relevant laws and regulations to ensure they are compliant and operating within the law.